Unlocking "The Secrets Of Effective Company Compliance"
Introduction
Company compliance is the bedrock of ethical and lawful business conduct, ensuring adherence to regulations, standards, and industry guidelines. In a dynamic global landscape, the importance of robust compliance measures cannot be overstated. It encompasses a comprehensive framework that spans legal, ethical, and operational dimensions, safeguarding the organization from risks while fostering a culture of integrity.
In this era of heightened regulatory scrutiny, businesses face complex challenges that demand a proactive and adaptive approach to compliance. From financial regulations to data protection laws, compliance serves as a shield, shielding companies from legal repercussions, reputational damage, and financial losses.
Effective company compliance involves continuous monitoring, assessment, and adjustment to align with evolving regulatory landscapes. It requires collaboration across departments, from legal and finance to operations and human resources. The commitment to compliance extends beyond avoiding penalties; it reflects an organization’s dedication to ethical business practices, stakeholder trust, and long-term sustainability.
This introduction underscores the multifaceted nature of company compliance, emphasizing its pivotal role in sustaining ethical business operations, mitigating risks, and contributing to the overall success and resilience of a company in the ever-evolving and intricate business environment..

Ensuring adherence to local, national, and international laws relevant to the industry is a cornerstone of effective corporate compliance. Companies operate within a complex legal landscape that spans different jurisdictions and regulatory frameworks. The commitment to compliance with these laws is crucial for maintaining legal standing, fostering ethical conduct, and mitigating risks. Here’s an in-depth explanation of this principle:
1. Local Compliance:
- Companies must comply with laws specific to the regions or municipalities in which they operate. Local regulations cover a spectrum of issues, including zoning laws, licensing requirements, and other region-specific legal nuances. Adhering to these laws ensures that businesses operate within the bounds set by local authorities.
2. National Compliance:
- National laws provide a foundational framework for businesses, encompassing areas such as taxation, employment practices, consumer protection, and industry-specific regulations. Compliance at the national level is essential for maintaining legal standing, avoiding penalties, and fostering a positive relationship with regulatory bodies.
3. International Compliance:
- Companies engaged in international business must navigate the diverse legal frameworks of different countries. This includes adherence to trade agreements, customs regulations, and international business laws. Multinational corporations, in particular, face the challenge of harmonizing operations with the laws of various nations, requiring a nuanced understanding of global legal intricacies.
4. Industry-Specific Regulations:
- Many industries are subject to specialized regulations that govern their operations. These industry-specific laws often address safety standards, environmental considerations, and other sector-specific requirements. Adherence to these regulations is not only a legal obligation but also a means of ensuring the responsible and sustainable functioning of the industry.
5. Risk Mitigation:
- Non-compliance with local, national, or international laws exposes companies to legal, financial, and reputational risks. Legal penalties, fines, and damage to the company’s reputation can result from failure to comply. By prioritizing adherence to applicable laws, businesses actively mitigate these risks and create a foundation for sustainable growth.
6. Ethical Considerations:
- Beyond the legal imperative, adhering to laws is a demonstration of ethical business conduct. Ethical behavior goes beyond what is legally required, reflecting a commitment to integrity and responsible corporate citizenship. Embracing this ethical dimension of compliance contributes to building trust with stakeholders and enhancing the company’s reputation.
7. Global Business Standards:
- In an era of globalized business, companies are increasingly held to global business standards and principles. Adhering to international laws and agreements fosters a positive image, attracting customers, investors, and partners who prioritize socially responsible and ethically sound business practices.
In conclusion, ensuring adherence to local, national, and international laws is not only a legal necessity but also a strategic imperative for businesses. This commitment establishes a framework for ethical conduct, risk mitigation, and responsible global citizenship, positioning companies for sustainable success in an increasingly interconnected and regulated business environment.

Complying with industry-specific regulations, as imposed by regulatory bodies or government agencies overseeing particular sectors, is a fundamental aspect of corporate governance and responsible business conduct. Industry-specific regulations are designed to address unique challenges, ensure safety, and maintain ethical standards within specific sectors. Here’s a comprehensive explanation of the significance and implications of adhering to these regulations:
1. Sector-Specific Nuances:
- Different industries face distinct challenges and risks that require tailored regulatory frameworks. Regulations can cover a wide range of issues, including product safety, environmental impact, labor practices, and quality standards. Compliance ensures that companies operate within the parameters defined by authorities familiar with the nuances of the industry.
2. Safety and Quality Standards:
- Industry-specific regulations often prioritize safety and quality standards. This can include measures to ensure the safety of products, processes, or services offered by companies. Compliance with these standards is essential to safeguarding consumers, employees, and stakeholders from potential harm.
3. Environmental Sustainability:
- Industries with environmental impacts, such as manufacturing or energy, are subject to regulations aimed at promoting sustainability and minimizing ecological harm. Compliance involves adopting eco-friendly practices, managing waste responsibly, and adhering to emissions standards to mitigate the environmental footprint of business operations.
4. Consumer Protection:
- Many industry-specific regulations focus on consumer protection. This includes measures to prevent fraud, ensure fair business practices, and provide accurate product information. Compliance contributes to building consumer trust by demonstrating a commitment to transparent and ethical dealings.
5. Labor Practices and Employee Rights:
- Regulations governing labor practices and employee rights are common in various industries. Compliance entails fair employment practices, adherence to working-hour regulations, and the provision of safe working conditions. Prioritizing compliance in this regard fosters a positive workplace culture and mitigates risks associated with labor-related disputes.
6. Innovation and Research Standards:
- Industries heavily involved in innovation and research, such as pharmaceuticals or technology, often face specific regulations to ensure the ethical and responsible development of new products or technologies. Compliance in these areas requires adherence to research ethics, data privacy standards, and intellectual property laws.
7. Financial Regulations:
- Certain industries, especially in the financial sector, are subject to specific regulations aimed at ensuring transparency, preventing fraud, and maintaining the stability of financial markets. Compliance involves adherence to accounting standards, disclosure requirements, and regulatory reporting.
8. Competitive Fairness:
- Industry-specific regulations also contribute to maintaining a level playing field among businesses within a particular sector. Compliance ensures that companies compete fairly, preventing unfair advantages that could arise from unethical or non-compliant practices.
9. Reputation and Stakeholder Trust:
- Adhering to industry-specific regulations enhances a company’s reputation and builds trust with stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulatory authorities. Compliance signals a commitment to ethical conduct, responsible business practices, and the overall well-being of the industry and its participants.
In conclusion, complying with industry-specific regulations is vital for ensuring the responsible and sustainable functioning of businesses within particular sectors. It fosters a culture of ethical conduct, safeguards stakeholders, and contributes to the overall health and integrity of the industry. Companies that prioritize industry-specific compliance not only meet legal requirements but also position themselves as responsible corporate citizens in their respective sectors.

Adhering to accounting standards, financial reporting requirements, and regulations is crucial for maintaining accurate and transparent financial records within a company. This compliance ensures that financial information is reliable, comparable, and understandable, facilitating trust among stakeholders such as investors, creditors, regulators, and the broader public.
Accounting standards, such as the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), provide a framework for recording and presenting financial information. These standards establish uniformity in financial reporting, allowing for consistent interpretation of a company’s performance. Compliance with these standards is essential for meaningful financial analysis and benchmarking against industry peers.
Financial reporting requirements, often mandated by regulatory bodies or stock exchanges, dictate the format and content of financial statements. These reports, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, offer a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health. Adhering to reporting requirements ensures that stakeholders receive timely and relevant information, fostering informed decision-making.
Regulations related to financial reporting serve multiple purposes. They safeguard the interests of investors by promoting transparency and disclosure. Regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States, enforce compliance to prevent fraudulent activities and ensure fair and efficient markets. Companies that fail to comply with these regulations may face legal consequences and damage to their reputation.
Maintaining accurate and transparent financial records goes beyond regulatory compliance; it reflects a commitment to integrity and ethical business practices. It enables management to assess the company’s financial position accurately, aiding strategic decision-making. Furthermore, transparent financial reporting enhances the company’s credibility, attracting investment and fostering long-term relationships with stakeholders.
In summary, adherence to accounting standards, financial reporting requirements, and regulations is imperative for a company’s financial integrity. It instills confidence in stakeholders, facilitates informed decision-making, and contributes to the overall stability and sustainability of the business.

Upholding ethical standards and business conduct is a fundamental aspect of responsible corporate governance, often articulated in a company’s code of ethics or conduct. This guiding document serves as a roadmap for employees, outlining the organization’s commitment to integrity, transparency, and ethical decision-making in all aspects of its operations.
A code of ethics typically begins by emphasizing the company’s core values and principles. These values may include honesty, respect, fairness, and social responsibility. By articulating these principles, the code establishes a moral foundation that guides employees in their daily activities and interactions, fostering a positive corporate culture.
Ethical standards outlined in a code of conduct provide clear expectations for employees regarding their behavior both within and outside the workplace. This includes interactions with colleagues, clients, suppliers, and the broader community. Employees are encouraged to act in a manner that upholds the company’s reputation and promotes trust among stakeholders.
One key aspect of ethical business conduct is the prohibition of activities such as fraud, corruption, bribery, and conflicts of interest. The code typically provides guidelines on gifts and entertainment, ensuring that such exchanges do not compromise objectivity or influence decision-making. It also stresses the importance of fair competition, encouraging employees to compete ethically and avoid anticompetitive practices.
A code of ethics often addresses issues related to confidentiality and data protection. Employees are expected to handle sensitive information responsibly and maintain the privacy of individuals and entities associated with the business. This ensures that the company complies with legal requirements and builds a foundation of trust with customers and partners.
The code of ethics is not merely a set of rules but a framework that encourages employees to speak up if they witness unethical behavior. Whistleblower protection mechanisms are often included to ensure that individuals reporting misconduct are shielded from retaliation, fostering a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.
By upholding ethical standards outlined in the code of ethics, companies can enhance their reputation, build trust with stakeholders, and create a positive working environment. Ethical behavior is not just a legal requirement but a crucial element in establishing a sustainable and socially responsible business that contributes positively to the community and the wider global context.

Adhering to environmental laws and regulations is imperative for businesses seeking to minimize their ecological impact and contribute to sustainable practices. These laws are designed to address various environmental concerns, including air and water quality, waste management, and biodiversity conservation. By complying with these regulations, companies can play a crucial role in preserving the environment and mitigating the negative effects of their operations.
Environmental laws typically set standards and restrictions on activities that could harm the environment. Adherence to these laws requires companies to monitor and control their emissions, waste disposal methods, and resource usage. This helps prevent pollution, conserve natural resources, and protect ecosystems. For example, regulations may dictate limits on greenhouse gas emissions, mandate responsible water usage, and require the proper disposal of hazardous waste.
Compliance with environmental laws also involves obtaining permits and approvals before undertaking certain activities. This process ensures that businesses thoroughly assess and mitigate potential environmental risks associated with their operations. It promotes transparency and accountability, as companies are required to disclose information about their environmental performance.
Beyond legal obligations, embracing environmental sustainability aligns with corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. Many businesses recognize the importance of adopting eco-friendly practices to meet the expectations of environmentally conscious consumers, investors, and communities. Proactive environmental management not only reduces the risk of legal consequences but also enhances a company’s reputation and brand value.
Implementing environmentally friendly practices often leads to operational efficiencies and cost savings. For instance, energy-efficient technologies, waste reduction measures, and sustainable supply chain practices can contribute to both environmental conservation and economic benefits. This dual impact reinforces the business case for environmentally responsible practices.
In conclusion, adhering to environmental laws and regulations is a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to minimize their ecological impact. Such compliance not only helps mitigate environmental risks but also aligns with societal expectations for responsible and sustainable business practices. By integrating environmental considerations into their operations, companies contribute to the broader goal of achieving ecological sustainability while simultaneously securing long-term viability and positive stakeholder relationships.

Ensuring a safe and healthy working environment for employees is a paramount responsibility for businesses, and compliance with occupational health and safety (OHS) regulations is central to achieving this objective. The well-being of employees is not only an ethical imperative but also contributes to a productive and sustainable workplace.
Occupational health and safety regulations set forth by government agencies establish standards and guidelines to protect workers from workplace hazards. Compliance with these regulations involves a comprehensive approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with job tasks and workplace conditions. By adhering to OHS regulations, companies aim to prevent accidents, injuries, and illnesses, creating a secure environment conducive to employee well-being and productivity.
Key aspects of compliance with OHS regulations include:
Risk Assessment: Conducting thorough assessments of workplace hazards to identify potential risks to employee health and safety. This involves analyzing processes, equipment, and work environments to implement appropriate preventive measures.
Safety Training: Providing employees with the necessary training and education on safety protocols, emergency procedures, and the proper use of equipment. Well-informed employees are better equipped to navigate potential hazards and respond to emergencies effectively.
Protective Measures: Implementing measures such as personal protective equipment (PPE), safety barriers, ventilation systems, and ergonomic workstations to minimize the risk of injuries and exposure to harmful substances.
Emergency Preparedness: Developing and regularly practicing emergency response plans to ensure that employees know how to react in the event of accidents, fires, or other emergencies. This includes evacuation procedures, first aid training, and access to emergency services.
Compliance Monitoring: Regularly monitoring and auditing workplace practices to ensure ongoing compliance with OHS regulations. This may involve inspections, safety audits, and the review of incident reports to identify areas for improvement.
Non-compliance with OHS regulations not only jeopardizes employee well-being but can also lead to legal consequences, financial penalties, and damage to the company’s reputation. Conversely, a commitment to creating a safe working environment demonstrates a company’s dedication to its employees and enhances its reputation as a socially responsible employer.
In conclusion, ensuring a safe and healthy working environment through compliance with occupational health and safety regulations is a fundamental obligation for businesses. Beyond legal requirements, it fosters a culture of care, promotes employee satisfaction, and contributes to overall organizational success by reducing absenteeism, improving morale, and enhancing productivity.

Adhering to labor laws and regulations is essential for businesses to maintain fair employment practices, regulate working hours, and safeguard employee rights. Labor laws are designed to create a balanced and equitable relationship between employers and employees, ensuring a work environment that promotes dignity, respect, and fairness.
Fair employment practices are a cornerstone of labor laws, encompassing principles such as non-discrimination, equal opportunities, and diversity in the workplace. Companies must comply with regulations that prohibit discrimination based on factors such as race, gender, age, disability, religion, or other protected characteristics. Establishing fair hiring practices and promoting a workplace free from harassment or retaliation is critical for fostering a positive and inclusive organizational culture.
Working hours and overtime regulations are crucial components of labor laws, intended to prevent employee exploitation and ensure a reasonable work-life balance. Compliance with these regulations involves setting standard working hours, specifying overtime compensation, and providing adequate rest periods. This helps prevent burnout, fatigue, and the potential negative impact on employees’ health and well-being.
Employee rights, as outlined in labor laws, cover various aspects of the employer-employee relationship. This includes the right to a safe workplace, protection from unfair labor practices, the right to organize and engage in collective bargaining, and entitlement to fair wages and benefits. Employers must adhere to regulations related to minimum wage laws, overtime pay, and the provision of benefits such as health insurance and leave policies.
Compliance with labor laws is not just a legal requirement; it contributes to building a positive employer brand and enhancing the overall employee experience. Companies that prioritize fair employment practices and respect labor regulations often enjoy higher employee satisfaction, loyalty, and productivity.
Non-compliance with labor laws can result in legal consequences, including fines, lawsuits, and damage to the company’s reputation. Additionally, organizations may face challenges in attracting and retaining talent if their employment practices are perceived as unfair or unethical.
In conclusion, adhering to labor laws and regulations is vital for businesses to establish a fair, respectful, and legally compliant working environment. This commitment not only fosters a positive workplace culture but also ensures the well-being and rights of employees, contributing to the overall success and sustainability of the organization.

Preventing corrupt practices and complying with anti-corruption laws, such as the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) in the United States or the UK Bribery Act, is essential for companies aiming to uphold ethical standards, build trust, and ensure fair business practices on a global scale. These laws are designed to combat corruption, bribery, and unethical conduct in business dealings, promoting transparency and integrity.
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) is a U.S. legislation that prohibits bribery of foreign officials to obtain or retain business. It also mandates accurate record-keeping and internal controls to prevent corrupt practices within organizations. The UK Bribery Act, on the other hand, applies to both domestic and international bribery and encompasses offenses related to giving, receiving, and bribing public and private entities.
Preventing corrupt practices begins with establishing a robust anti-corruption compliance program within an organization. This includes:
Risk Assessment: Conducting a thorough assessment to identify areas of potential corruption risk in business operations, partnerships, and third-party relationships.
Policies and Procedures: Developing and implementing comprehensive anti-corruption policies and procedures that align with the requirements of relevant anti-corruption laws.
Training and Communication: Providing regular training sessions to employees at all levels to ensure a clear understanding of anti-corruption policies and the consequences of non-compliance. Open communication channels also encourage employees to report any suspected corrupt practices.
Due Diligence: Conducting due diligence on third-party partners, agents, and intermediaries to ensure they adhere to anti-corruption laws and ethical standards.
Monitoring and Reporting: Implementing monitoring mechanisms to track compliance with anti-corruption policies and establishing reporting channels for employees to raise concerns or report potential violations.
Enforcement and Disciplinary Measures: Enforcing a zero-tolerance policy for corrupt practices and implementing disciplinary measures for employees engaging in unethical conduct.
Compliance with anti-corruption laws not only mitigates legal risks but also enhances a company’s reputation and credibility. Non-compliance can result in severe consequences, including fines, legal actions, damage to the brand, and even imprisonment for individuals involved.
In conclusion, preventing corrupt practices and complying with anti-corruption laws is a strategic imperative for companies operating in the global marketplace. Such efforts not only contribute to the fight against corruption but also position businesses as ethical and trustworthy entities, fostering sustainable and responsible business practices..

Complying with industry-specific quality standards is essential for businesses seeking to ensure the consistent quality of their products or services. These standards serve as benchmarks, providing a framework for companies to meet or exceed specific criteria, ultimately contributing to customer satisfaction, regulatory compliance, and overall competitiveness within their respective industries.
Industry-specific quality standards are developed to address the unique requirements and expectations of a particular sector. These standards may cover various aspects, including design, production, testing, safety, and performance. Adherence to these standards is not only a commitment to delivering high-quality products or services but also a demonstration of a company’s dedication to continuous improvement and customer-centricity.
Key elements of complying with industry-specific quality standards include:
Standardization of Processes: Quality standards often define standardized processes and methodologies for product development, manufacturing, and service delivery. By following these established procedures, companies can achieve consistency and reliability in their outputs.
Product Conformity: Meeting industry-specific quality standards ensures that products or services conform to recognized benchmarks. This conformity is critical for meeting customer expectations and building trust in the brand.
Risk Mitigation: Quality standards incorporate risk management principles, helping companies identify potential issues early in the production or service delivery process. This proactive approach allows for the mitigation of risks related to defects, safety concerns, and regulatory non-compliance.
Customer Satisfaction: Adherence to quality standards directly impacts customer satisfaction. Consistently delivering products or services that meet or exceed industry benchmarks enhances customer trust, loyalty, and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Regulatory Compliance: Many industry-specific quality standards are intertwined with regulatory requirements. Compliance not only satisfies legal obligations but also minimizes the risk of legal consequences and ensures a company’s license to operate.
Competitive Advantage: Conforming to quality standards can provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Certification or recognition for meeting industry benchmarks can differentiate a company from competitors and attract discerning customers.
Continuous improvement is often a core principle within quality standards. This involves monitoring performance, analyzing data, and implementing corrective actions to enhance processes and outcomes. By embracing a culture of quality, companies position themselves to adapt to changing market conditions, emerging technologies, and evolving customer expectations.
In summary, complying with industry-specific quality standards is a strategic investment for companies, fostering consistency, reliability, and customer satisfaction. It aligns businesses with best practices, regulatory requirements, and market expectations, contributing to long-term success and competitiveness in their respective industries.
Ensuring ethical and legal practices within the supply chain is imperative for companies aiming to uphold their corporate responsibility, mitigate risks, and build a sustainable and positive reputation. This commitment extends to various aspects, including fair labor practices, environmental sustainability, and responsible sourcing.
Fair Labor Practices: Ethical supply chain management involves treating workers with dignity and ensuring fair labor practices throughout the entire supply chain. This includes adherence to international labor standards, fair wages, reasonable working hours, and the prohibition of child labor and forced labor. Companies should implement and enforce codes of conduct for suppliers, conduct regular audits, and provide transparent reporting on labor practices.
2. Environmental Sustainability: Responsible supply chain practices also entail minimizing the environmental impact of operations. Companies should adopt eco-friendly measures, such as reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and using sustainable materials. Compliance with environmental regulations and obtaining certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management demonstrates a commitment to sustainable practices and ensures the long-term health of ecosystems.
3. Responsible Sourcing: Ensuring ethical practices within the supply chain extends to responsible sourcing of materials and components. This involves evaluating and selecting suppliers based not only on cost and quality but also on their ethical and social responsibility practices. Companies can implement due diligence processes, traceability systems, and supplier assessments to ensure that their sourcing practices align with ethical standards.
4. Compliance with Legal Standards: Adherence to local and international laws and regulations is a fundamental aspect of ethical supply chain management. This includes compliance with labor laws, environmental regulations, and anti-corruption laws. Regular legal audits and monitoring of regulatory changes help companies stay informed and ensure ongoing compliance.
5. Collaboration and Transparency: Building ethical supply chains often involves collaboration and transparency among all stakeholders. Companies should engage with suppliers, workers, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and other partners to address ethical challenges collectively. Transparent communication about supply chain practices, challenges, and improvements fosters trust among stakeholders and demonstrates a commitment to accountability.
By implementing ethical supply chain practices, companies not only meet legal obligations but also contribute to sustainable development, social justice, and environmental conservation. Additionally, ethical supply chain management can enhance brand reputation, attract conscious consumers, and mitigate potential risks associated with unethical practices, ultimately contributing to the long-term success and resilience of the business.

Adhering to principles of corporate governance is crucial for establishing a framework that promotes transparency, accountability, and effective decision-making within an organization. These principles guide the relationships and responsibilities among the various stakeholders, emphasizing ethical conduct and sustainable business practices.
Board Structure and Functioning: Corporate governance principles advocate for the establishment of a well-structured and independent board of directors. The board plays a central role in overseeing the company’s management, strategy, and performance. It is typically composed of a mix of executive and non-executive directors, with independent directors providing objective oversight. Boards are responsible for making key decisions, setting strategic direction, and ensuring that the company operates in the best interest of shareholders and other stakeholders.
2. Transparency: Transparency is a cornerstone of effective corporate governance. Companies are expected to provide clear and comprehensive information to stakeholders regarding their financial performance, strategic goals, and risk management. This includes regular and timely financial reporting, disclosure of material information, and transparent communication about corporate policies and practices. Transparency builds trust among investors, customers, employees, and the wider public.
3. Accountability: Accountability is fundamental to corporate governance and involves holding individuals and entities responsible for their actions and decisions. This extends to the board of directors, executive leadership, and all employees. Effective corporate governance establishes mechanisms for accountability, such as performance evaluations, ethical guidelines, and checks and balances within the organization. Boards are accountable to shareholders, ensuring that their decisions align with the company’s long-term interests.
4. Ethical Conduct: Corporate governance principles emphasize ethical behavior throughout the organization. This includes promoting a culture of integrity, fairness, and responsibility. Companies are expected to establish and enforce a code of ethics that guides the behavior of all employees and stakeholders. Ethical conduct not only aligns with societal expectations but also helps prevent fraudulent activities and reputational damage.
5. Shareholder Rights: Corporate governance principles advocate for protecting the rights of shareholders. This includes ensuring fair treatment, equitable access to information, and the ability to exercise voting rights. Shareholders should have the opportunity to voice their concerns, participate in important decisions, and hold the board accountable through mechanisms such as annual meetings.
In summary, adherence to principles of corporate governance establishes a framework that fosters transparency, accountability, and ethical behavior within an organization. This commitment enhances trust among stakeholders, contributes to long-term sustainability, and positions the company for success in a dynamic business environment. Effective corporate governance is not only a regulatory requirement but also a strategic imperative for responsible and resilient business operations.

Incorporating socially responsible practices, encompassing community engagement, philanthropy, and sustainability initiatives, is a pivotal aspect of corporate citizenship that goes beyond profit-making to contribute positively to society and the environment. This approach, often referred to as corporate social responsibility (CSR), reflects a company’s commitment to ethical conduct, environmental stewardship, and the well-being of the communities in which it operates.
1. Community Engagement: Socially responsible companies actively engage with the communities they serve. This involvement extends beyond business operations to understanding and addressing local needs. Community engagement initiatives may include supporting local education, healthcare, and infrastructure projects. Establishing partnerships with local organizations and involving employees in volunteer programs are common strategies for building strong relationships and making a positive impact.
2. Philanthropy: Philanthropy is a key component of CSR, involving the donation of resources, funds, or expertise to charitable causes. Companies may support nonprofit organizations, charities, or social initiatives aligned with their values and community needs. This can take the form of financial contributions, in-kind donations, or employee volunteerism. Philanthropic efforts often focus on addressing societal challenges such as poverty, hunger, education, and healthcare.
3. Sustainability Initiatives: Sustainability is integral to socially responsible practices, addressing environmental concerns and promoting responsible resource management. Companies incorporate sustainability initiatives to reduce their ecological footprint, adopt eco-friendly practices, and contribute to the global effort to combat climate change. This may involve adopting renewable energy sources, minimizing waste, and implementing green technologies throughout the supply chain.
4. Ethical Supply Chain Practices: Social responsibility extends to the entire supply chain, emphasizing fair labor practices, human rights, and responsible sourcing. Companies committed to ethical supply chain practices ensure that their business operations do not contribute to labor exploitation, child labor, or environmental degradation. This includes conducting regular audits of suppliers and promoting fair trade principles.
5. Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, and regulatory bodies, is a vital aspect of socially responsible practices. Transparent communication about CSR initiatives, sustainability goals, and ethical conduct fosters trust and accountability. Listening to and considering the perspectives of various stakeholders ensures that corporate actions align with broader societal expectations.
In conclusion, incorporating socially responsible practices is an integral part of modern business strategies. Beyond financial success, companies that embrace CSR contribute to positive social and environmental outcomes. This approach not only aligns with ethical standards but also enhances brand reputation, attracts socially conscious consumers, and positions businesses as responsible contributors to a better and more sustainable world.

Adhering to standards and regulations to protect an organization’s information systems and data from cyber threats is a critical component of cybersecurity. As the digital landscape evolves, businesses face increasing risks from cybercriminals seeking unauthorized access, data breaches, and disruptions to operations. Compliance with established standards and regulations provides a framework to mitigate these risks and safeguard sensitive information.
Cybersecurity Standards: Adhering to widely recognized cybersecurity standards, such as ISO/IEC 27001 or NIST Cybersecurity Framework, establishes a systematic and comprehensive approach to information security. These standards provide guidelines for developing, implementing, and continuously improving information security management systems. Compliance ensures that organizations follow best practices to protect their data and information systems.
2. Data Protection Regulations: Data protection regulations, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), impose legal obligations on organizations regarding the collection, storage, and processing of personal and sensitive data. Compliance includes implementing measures to secure data, ensuring consent for data processing, and promptly notifying authorities and affected individuals in case of a data breach.
3. Network Security Compliance: Adherence to network security standards is crucial for protecting an organization’s digital infrastructure. Compliance with regulations such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) ensures the secure processing of payment transactions. This includes implementing firewalls, encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments to safeguard financial data.
4. Employee Training and Awareness: Standards and regulations often emphasize the importance of employee training and awareness in cybersecurity. Human error is a significant factor in cyber incidents, and compliance requires organizations to educate employees on cybersecurity best practices, phishing awareness, and the importance of strong password management.
5. Incident Response Planning: Standards and regulations often mandate the development and testing of incident response plans. These plans outline procedures to be followed in the event of a cybersecurity incident, facilitating a swift and effective response to mitigate the impact, contain the threat, and restore normal operations.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Auditing: Compliance involves continuous monitoring of information systems for potential threats and vulnerabilities. Regular security audits and assessments ensure that the organization’s cybersecurity measures remain effective and aligned with evolving threats and technology advancements.
Non-compliance with cybersecurity standards and regulations can result in severe consequences, including financial penalties, legal actions, and reputational damage. Conversely, a proactive and compliant approach to cybersecurity not only protects the organization’s assets but also instills confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders.
In conclusion, adhering to standards and regulations in cybersecurity is essential for organizations to establish a robust defense against evolving cyber threats. By following these guidelines, companies can create a resilient cybersecurity posture that protects their information systems and data, demonstrating a commitment to responsible and secure business practices.

Ensuring that products, services, and digital content are accessible to individuals with disabilities is not only a legal requirement in many jurisdictions but also a fundamental aspect of promoting inclusivity and equal opportunities. Compliance with accessibility standards is essential for creating an environment where everyone, regardless of their abilities, can fully participate in various aspects of life, including education, employment, and social interactions.
Legal Compliance: Many countries, including the United States with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the European Union with the Web Accessibility Directive, have established legal frameworks that mandate accessibility in various domains. Compliance with these laws is not only a legal obligation but also a way for businesses to contribute to a more inclusive society.
2. Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG): The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), are widely recognized as the standard for web accessibility. Adhering to WCAG ensures that digital content, including websites and applications, is perceivable, operable, and understandable for individuals with disabilities. This includes providing alternatives for non-text content, ensuring keyboard accessibility, and designing content that is navigable by screen readers.
3. Product and Service Accessibility: Accessibility standards extend beyond digital content to encompass physical products and services. For example, buildings, transportation systems, and public spaces are increasingly designed with features that facilitate access for individuals with mobility, vision, or hearing impairments. Ensuring that products and services are universally designed promotes usability for all users.
4. Inclusive Design Principles: Compliance with accessibility standards aligns with the principles of inclusive design, emphasizing the creation of products and services that can be used by the widest range of individuals. This approach encourages businesses to consider diverse user needs and preferences during the design and development process, resulting in solutions that are more intuitive, flexible, and accommodating.
5. Assistive Technologies Compatibility: Accessibility standards also address compatibility with assistive technologies such as screen readers, voice recognition software, and alternative input devices. Designing products and digital content to work seamlessly with these technologies enhances the overall accessibility of the user experience.
Failure to comply with accessibility standards not only poses legal risks but also limits the reach and usability of products and services. In contrast, businesses that prioritize accessibility demonstrate a commitment to diversity and social responsibility, while also tapping into a broader market by making their offerings accessible to a more extensive and diverse audience.
In conclusion, ensuring accessibility for individuals with disabilities by complying with standards is a foundational element of creating an inclusive and equitable society. Embracing these standards not only meets legal requirements but also reflects a commitment to fostering accessibility, diversity, and equal opportunities for all individuals, regardless of their abilities.
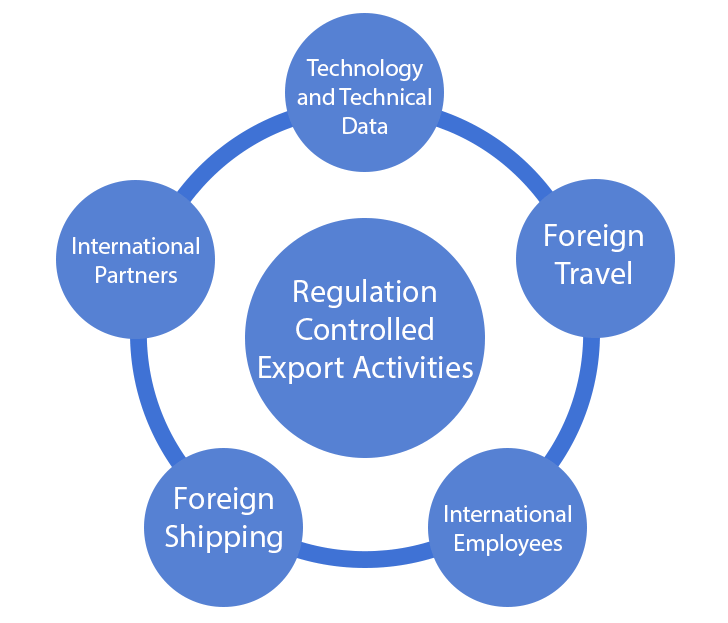
Complying with regulations governing the export of goods and services, particularly trade sanctions and embargoes, is essential for businesses engaged in international trade. These regulations are implemented by governments to achieve various policy objectives, including national security, foreign policy goals, and the promotion of human rights. Adherence to export control regulations helps maintain global stability and prevents the unintended consequences of improper trade activities.
Trade Sanctions and Embargoes: Trade sanctions and embargoes are restrictive measures imposed by governments to limit or prohibit trade with specific countries or entities. These measures can be comprehensive, targeting an entire country, or more targeted, focusing on specific individuals, organizations, or sectors. Complying with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal consequences and penalties.
2. Restricted Parties Screening: One key aspect of compliance with export regulations involves conducting thorough due diligence through restricted parties screening. This process ensures that businesses do not engage in transactions with individuals or entities subject to sanctions or embargoes. Implementing robust screening mechanisms helps organizations identify and avoid dealings with restricted parties.
3. Export Licensing: In many jurisdictions, certain goods, technologies, and services are subject to export controls, requiring businesses to obtain appropriate licenses before exporting them. Compliance involves understanding the specific export licensing requirements for the products or services in question and obtaining the necessary approvals from relevant authorities.
4. Dual-Use Items: Export regulations often address dual-use items—goods, technologies, or software that can have both civilian and military applications. Businesses must be aware of the export controls on dual-use items and comply with licensing requirements to prevent the unintended proliferation of sensitive technologies.
5. Compliance Management Systems: Establishing a robust compliance management system is essential for navigating the complexities of export regulations. This includes developing internal procedures, conducting employee training, and implementing effective monitoring and auditing mechanisms to ensure ongoing compliance.
6. Risk Assessment: Conducting regular risk assessments helps businesses identify potential vulnerabilities in their export processes. This involves assessing the risk of inadvertently violating export regulations, especially when dealing with complex global supply chains and diverse business partners.
Non-compliance with export regulations can lead to severe consequences, including fines, penalties, and damage to the organization’s reputation. Additionally, businesses may face legal actions and restrictions on their ability to conduct international trade.
In conclusion, complying with regulations governing the export of goods and services, particularly trade sanctions and embargoes, is critical for businesses operating in the global marketplace. A proactive approach to understanding and adhering to these regulations not only ensures legal compliance but also contributes to global stability and responsible business practices in the international arena.

Adhering to laws and regulations designed to protect consumers is a fundamental responsibility for businesses, contributing to fair and transparent business practices that build trust and foster positive relationships with customers. Consumer protection laws are established to safeguard the rights and interests of consumers, ensuring they are treated fairly, honestly, and without exploitation.
Fair and Transparent Transactions: Compliance with consumer protection laws requires businesses to engage in fair and transparent transactions. This includes providing accurate information about products and services, disclosing terms and conditions, and avoiding deceptive or misleading practices. Transparency in pricing, warranties, and return policies enhances consumer confidence and establishes a foundation of trust.
2. Product Safety and Quality: Businesses are obligated to adhere to regulations that govern the safety and quality of products offered to consumers. This involves ensuring that products meet specified safety standards, are appropriately labeled, and do not pose health or safety risks. Compliance in this area protects consumers from potential harm and reinforces the reputation of the business.
3. Privacy and Data Protection: Consumer protection laws also address the privacy and security of consumer data. Businesses must implement measures to safeguard personal information, obtain consent for data collection, and inform consumers about how their information will be used. This fosters trust by demonstrating a commitment to protecting consumer privacy.
4. Redress and Dispute Resolution: In the event of disputes or consumer grievances, businesses are required to have mechanisms for redress and dispute resolution. Compliance involves addressing customer complaints promptly and fairly, providing avenues for resolution, and honoring warranty or guarantee commitments. Responsive and customer-focused dispute resolution contributes to positive customer experiences.
5. Anti-Unfair Practices: Consumer protection laws prohibit unfair business practices that could exploit or harm consumers. This includes practices such as false advertising, bait-and-switch tactics, or unfair contract terms. Adherence to these regulations ensures that businesses compete fairly, and consumers are not subjected to deceptive or manipulative practices.
6. Education and Information: Businesses are encouraged to educate consumers about their rights and provide clear information about products and services. This empowers consumers to make informed choices and reinforces a commitment to ethical and consumer-friendly practices.
Compliance with consumer protection laws is not only a legal obligation but also a strategic imperative for businesses. Violations can result in legal consequences, financial penalties, and damage to the company’s reputation. On the contrary, businesses that prioritize consumer protection contribute to a marketplace characterized by fairness, integrity, and mutual respect.
In conclusion, adhering to laws and regulations designed to protect consumers is essential for businesses committed to fair and transparent practices. By prioritizing consumer rights, businesses not only comply with legal requirements but also build lasting relationships, enhance their reputation, and contribute to a marketplace that values and prioritizes consumer well-being.

Protecting and respecting intellectual property (IP) rights is a critical aspect of responsible business conduct, involving compliance with copyright, trademark, and patent laws. Intellectual property laws are designed to safeguard the creations and innovations of individuals and organizations, fostering innovation, creativity, and fair competition.
Copyright Laws: Copyright laws protect original works of authorship, such as literary, artistic, and musical creations. Compliance involves respecting the rights of creators and obtaining proper permissions or licenses before using or reproducing copyrighted material. This applies to a wide range of content, including written works, images, software, and audiovisual productions.
2. Trademark Laws: Trademark laws protect distinctive signs, symbols, or expressions that identify and distinguish products or services. Compliance with trademark laws involves respecting the trademarks of others and avoiding the unauthorized use of protected marks. This includes conducting thorough searches to ensure that the chosen trademarks do not infringe on existing registrations.
3. Patent Laws: Patent laws protect inventions and innovations, granting inventors exclusive rights to their discoveries for a specified period. Compliance requires businesses to respect existing patents, conduct thorough patent searches before developing new products, and apply for patents to protect their own inventions. Patent infringement can lead to legal consequences and financial penalties.
4. Trade Secrets: In addition to copyright, trademark, and patent laws, protecting trade secrets is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Compliance involves implementing measures to safeguard confidential business information, such as formulas, processes, or customer lists. Businesses must establish and enforce internal policies to prevent unauthorized access or disclosure of trade secrets.
5. Licensing and Agreements: Compliance with intellectual property laws often involves entering into licensing agreements to use or commercialize protected creations. These agreements outline the terms and conditions under which intellectual property can be utilized. Businesses must negotiate and adhere to these agreements to avoid legal disputes and ensure fair compensation to the IP owners.
6. Enforcement and Litigation: In the event of intellectual property disputes, compliance requires businesses to engage in ethical and legal means of dispute resolution. This may involve negotiating settlements, participating in alternative dispute resolution processes, or, if necessary, litigating to protect their own IP or defend against allegations of infringement.
Non-compliance with intellectual property laws can result in legal consequences, financial liabilities, and damage to the reputation of the business. Conversely, a commitment to protecting and respecting intellectual property rights fosters an environment of innovation, encourages creativity, and contributes to a fair and competitive marketplace.
In conclusion, compliance with copyright, trademark, and patent laws is essential for businesses to protect their intellectual property rights and contribute to a global ecosystem that values and incentivizes innovation. Respecting the rights of creators and innovators not only ensures legal compliance but also promotes a culture of creativity and responsible business practices.








